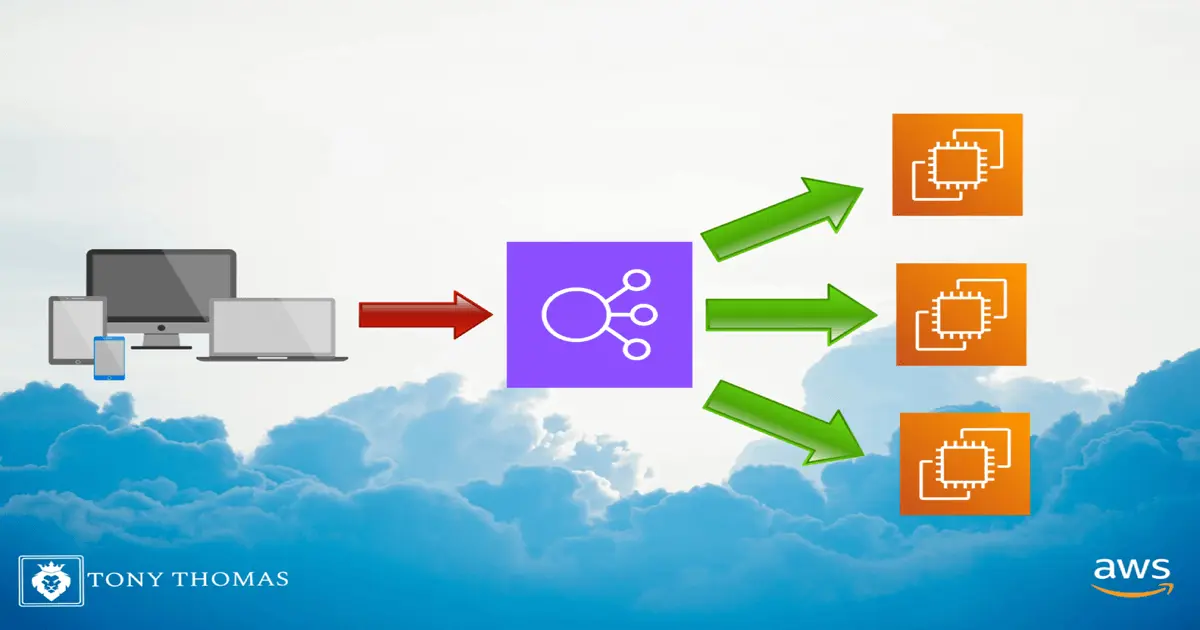
When building cloud applications, managing traffic efficiently is crucial. AWS Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) helps by distributing requests across multiple instances. It improves performance, prevents downtime, and ensures your apps remain available even during traffic spikes.
Table Of Content
- What is AWS Elastic Load Balancer?
- How Does ELB Work?
- Benefits of Using AWS Elastic Load Balancer
- Types of AWS Elastic Load Balancers
- 1. Application Load Balancer (ALB)
- 2. Network Load Balancer (NLB)
- 3. Classic Load Balancer (CLB)
- Setting Up an AWS Elastic Load Balancer
- Best Practices for AWS Load Balancers
- Monitoring and Optimization
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Conclusion
In this guide, you’ll learn what AWS ELB is, how it works, its types, and the best practices for implementation.
What is AWS Elastic Load Balancer?
An Elastic Load Balancer is a service from Amazon Web Services that automatically distributes incoming traffic across healthy resources, such as EC2 instances. Acting as a single point of access, it routes requests to backend instances while monitoring their health.
If one server fails, ELB directs traffic to healthy ones. This improves fault tolerance and ensures users get a smooth experience. ELB also scales automatically, handling millions of requests per second without manual effort.
Read the official AWS ELB documentation
How Does ELB Work?
When a user request arrives, it first hits the load balancer. Based on routing rules, ELB forwards it to an available backend instance. The response then returns to the client via the load balancer.
To maximize availability, AWS recommends spreading resources across multiple Availability Zones (AZs). ELB manages this automatically, so even if one AZ goes down, the application stays online.
Benefits of Using AWS Elastic Load Balancer
- High Availability – ELB routes traffic only to healthy servers, minimizing downtime.
- Scalability – It adjusts capacity automatically to handle traffic changes.
- Improved Performance – Requests are distributed evenly, reducing latency.
- Simplified Management – Monitoring and health checks are built in.
- Cost-Effective – Pay only for what you use, with no upfront investment.
Related post: AWS Auto Scaling Guide – Learn how ELB integrates with Auto Scaling.
Types of AWS Elastic Load Balancers
AWS offers three types of load balancers, each with unique features:
1. Application Load Balancer (ALB)
- Operates at Layer 7 (Application Layer).
- Best for HTTP and HTTPS traffic.
- Supports advanced routing (by URL, host, or headers).
- Ideal for microservices and container-based apps.
2. Network Load Balancer (NLB)
- Operates at Layer 4 (Transport Layer).
- Handles TCP, UDP, and TLS traffic with ultra-low latency.
- Suitable for gaming, streaming, or IoT workloads.
3. Classic Load Balancer (CLB)
- The first generation of AWS load balancers.
- Works at both Layer 4 and 7.
- Provides basic routing features.
- Recommended only for legacy apps.
Setting Up an AWS Elastic Load Balancer
You can create an ELB via the AWS Management Console:
- Create a Load Balancer – Choose ALB, NLB, or CLB.
- Configure Settings – Select VPC, subnets, and security groups.
- Register Targets – Add EC2 instances or containers to backend target groups.
- Set Routing Rules – Define how requests are directed.
- Configure Health Checks – Ensure only healthy instances get traffic.
- Enable Logging and Monitoring – Use CloudWatch for metrics and alarms.
Step-by-step guide: AWS Load Balancer Setup
Best Practices for AWS Load Balancers
- Distribute instances across AZs for fault tolerance.
- Enable HTTPS with SSL/TLS for secure connections.
- Tune health checks to detect failures quickly.
- Use Auto Scaling with ELB for automated capacity management.
- Review metrics regularly with CloudWatch dashboards.
Monitoring and Optimization
- CloudWatch Metrics – Track request counts, latency, and error rates.
- Access Logs – Store logs in Amazon S3 for analysis.
- Auto Scaling Integration – Scale backend instances automatically.
- Caching Support – Improve response times by serving cached content.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Unhealthy Instances – Check health check paths and security groups.
- High Latency – Review instance performance and routing rules.
- SSL Errors – Verify certificates and listener settings.
- Uneven Traffic Distribution – Ensure target groups are balanced correctly.
If problems persist, AWS documentation and support provide detailed troubleshooting steps.
Conclusion
AWS Elastic Load Balancer is a powerful tool for improving the availability, scalability, and performance of cloud applications. By distributing traffic intelligently, monitoring resources, and integrating with Auto Scaling, it simplifies infrastructure management while keeping costs under control.
Whether you’re running web apps, APIs, or large-scale workloads, ELB ensures your applications remain fast, secure, and reliable.